The telephone is a revolutionary invention that has dramatically transformed the way we communicate
with each other. It has evolved significantly since its inception in the 19th century, from its first crude form
to the sleek and sophisticated smartphones of today. In this article, we will explore the development
history of the phone, tracing its evolution from the first telegraph to the latest smartphones.
The earliest form of long-distance communication was the telegraph, which was invented in the early
19th century. The telegraph used electrical impulses to send messages over long distances, but it was a
cumbersome and slow process that required trained operators to interpret the signals. The invention of
the telephone in the late 19th century changed all that, making it possible to send voice messages over
long distances in real-time.
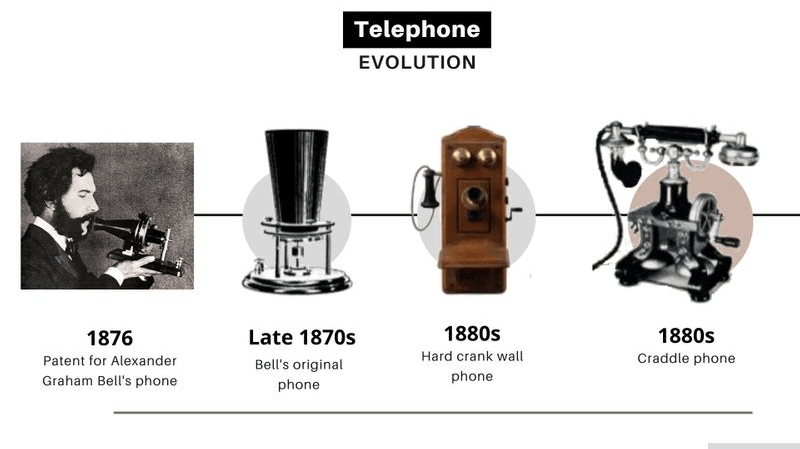
Alexander Graham Bell is credited with inventing the telephone in 1876, but the development of the
technology was a collaborative effort involving many inventors and engineers. Bell’s telephone was a
simple device that consisted of a transmitter, which converted sound waves into electrical signals, and a
receiver, which converted the electrical signals back into sound waves. The first phone call was made by
Bell to his assistant, Thomas Watson, on March 10, 1876, and the message transmitted was “Mr.
Watson, come here. I want to see you.”
Bell’s invention quickly caught on, and by the end of the century, there were over a million telephones in
use in the United States. The early telephones were large and bulky, with a separate transmitter and
receiver that were connected by a wire. The first telephones were also limited in range, and it was only
possible to communicate over short distances.
The development of the telephone network was a major milestone in the history of the phone. The first
telephone exchange was established in New Haven, Connecticut in 1878, and soon after, telephone
exchanges began to spring up in cities across the country. The telephone network allowed people to
communicate over long distances, making it possible to conduct business and stay in touch with friends
and family members who lived far away.
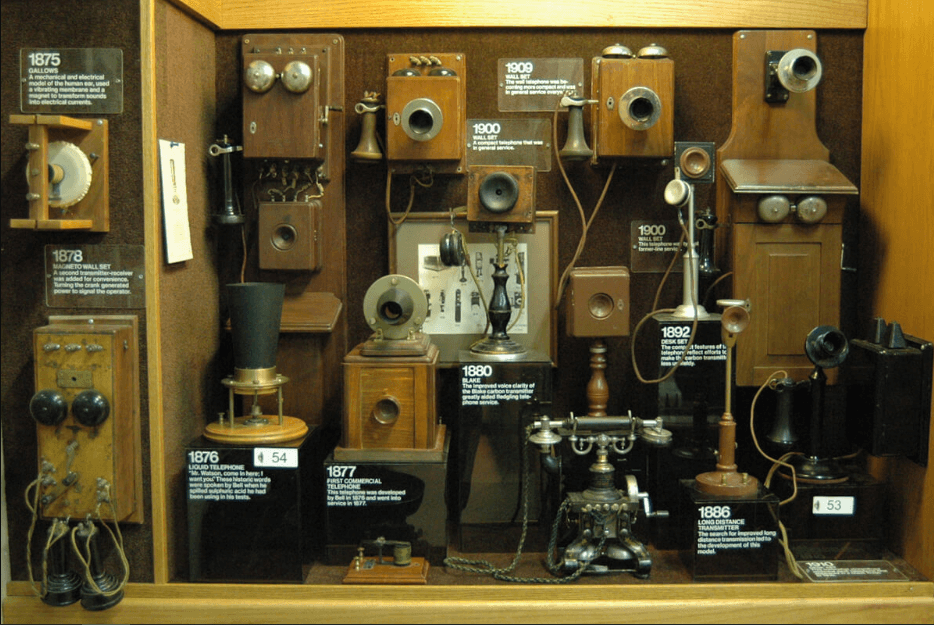
The early 20th century saw significant improvements in telephone technology. The first rotary dial phone
was introduced in 1904, which made it possible to dial phone numbers directly instead of having to ask
an operator to connect the call. The first automatic telephone exchange was introduced in 1915.
The 20th century saw even more significant developments in the field of telephony, with the introduction of new technologies that transformed the way we communicate. In the early 1900s, the first long- distance telephone lines were laid, connecting cities and countries and enabling people to communicate over vast distances.
In the 1920s, the first public payphones were introduced, allowing people to make calls from public
locations for a fee. This made it possible for people to stay connected even when they were away from
home or the office.
The 1930s saw the introduction of the first cordless telephones, which allowed people to move around
while they were on the phone. These early models were large and cumbersome, but they paved the way
for the development of the modern cordless phone.
During World War II, the telephone system played a vital role in communication between military forces.
The development of portable radios and walkie-talkies allowed soldiers to communicate with each other
over long distances, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of military operations.
In the post-war era, the telephone system continued to evolve, with new technologies being introduced to
make communication faster and more efficient. In the 1950s, the first direct-dial telephones were
introduced. The invention of the telephone is considered one of the most significant achievements in human history,
as it revolutionized the way people communicate with each other. The telephone, which was invented by
Alexander Graham Bell in 1876, allowed people to communicate with each other over long distances,
thereby eliminating the need for physical travel and enabling faster and more efficient communication.
The success of the telephone can be measured in many ways. From a technological standpoint, the
invention of the telephone paved the way for the development of other communication technologies,
such as radio and television, and eventually, the internet and smartphones.
From a societal standpoint, the telephone has had a profound impact on the way people interact with
each other, both personally and professionally. The telephone has made it easier for people to maintain
long-distance relationships, conduct business across different geographic locations, and stay connected
with friends and family members.
In terms of economic impact, the telephone has played a crucial role in the development of the
telecommunications industry, which has become one of the largest and most profitable industries in the
world. The telephone has also created many jobs and opportunities for people in the field of
telecommunications and related industries.
Overall, the success of the invention of the telephone is reflected in its widespread adoption and
continued use as a critical communication tool in today’s world.










